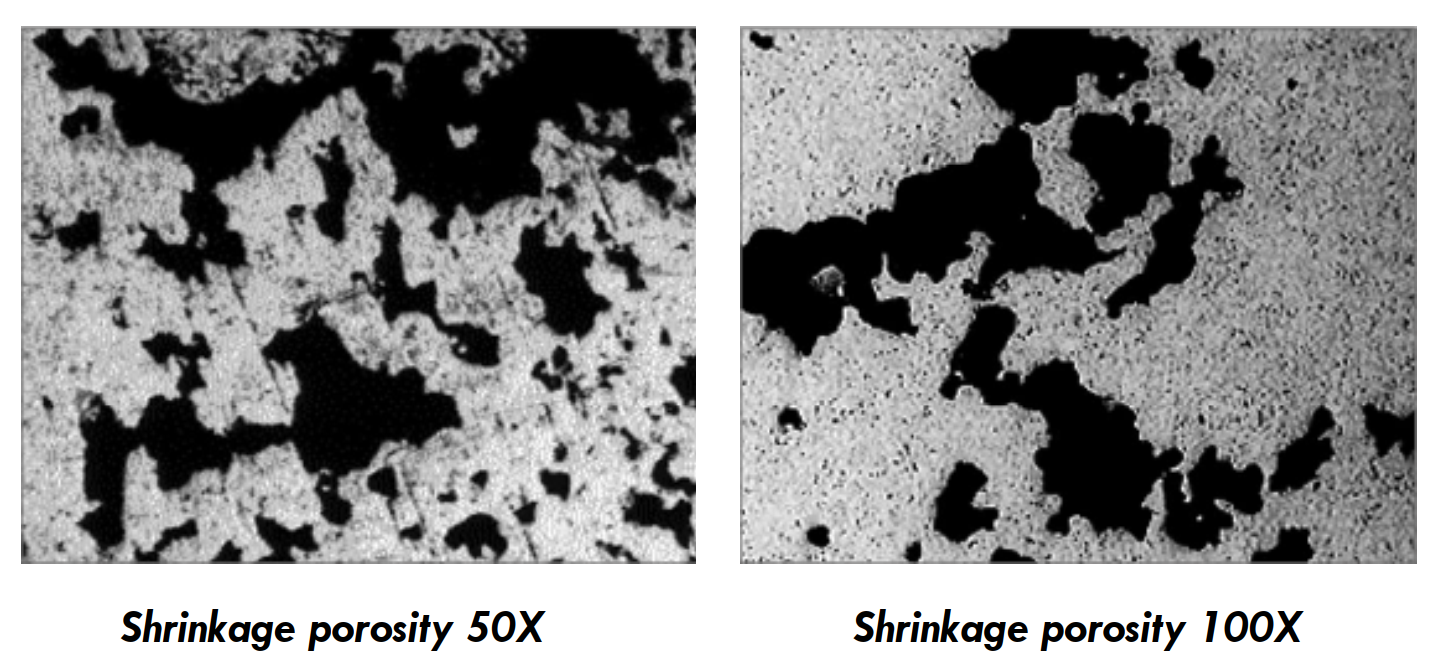
Gas porosity is one of the most common and challenging defects in the aluminum die-casting industry. It refers to the presence of gas pockets or voids within the metal structure, which can significantly affect the mechanical properties, appearance, and overall performance of the final product.

What Causes Gas Porosity?
Gas porosity in aluminum die-casting is primarily caused by:
- Entrapped air during the high-pressure injection process.
- Hydrogen absorption in molten aluminum, especially at high temperatures.
- Moisture in die lubricant or release agents breaking down and generating steam.
- Improper venting, where air is unable to escape the mold cavity efficiently.
How to Identify Gas Porosity
Detecting gas porosity early is crucial to maintaining high-quality production standards. Here are common identification methods:
- Visual Inspection
Surface-level porosity often appears as small holes, blisters, or rough patches. - X-ray Imaging
Used for detecting internal porosity that is not visible on the surface.
Impacts of Gas Porosity
- Reduces mechanical strength
- Weakens pressure tightness
- Affects machining precision
- Leads to increased scrap rates and rework costs
Prevention Methods
To reduce or eliminate gas porosity in aluminum die-casting, manufacturers in the industry die-casting sector can implement:
- Proper degassing of molten aluminum using rotary or GBF degassing units.
- Optimized gating system to reduce air entrapment.
- Control of die temperature and injection parameters.
- Use of vacuum systems or improved venting designs.
- High-quality die lubricants with minimal moisture content.
At PT Wilisindomas Indahmakmur, we support the aluminum industry die-casting with advanced solutions for process control, defect prevention, and performance improvement. Our team can assist you in identifying and minimizing gas porosity with the right tools and technical support.
Contact us today to learn more about our products and solutions for die-casting challenges.